Read More

Discover what’s next for AI in healthcare in 2026 - Get Access to the Full Report
ON THIS PAGE
- What is a Cloud App?
- Top Features of Cloud Apps
- Benefits of Cloud-Based Applications
- Limitations of Cloud-Based Applications
- Significant Use Cases of Cloud Apps
- What is a Web App?
- Top Features of Web Apps
- Benefits of Web Applications
- Limitations of Web Applications
- Significant Use Cases of Web Apps
- Web App vs Cloud App: A Quick Comparison
- Cloud App vs Web App: A Brief Table
- Cloud App vs Web App: Who Wins?
- Unlock the Best Option with Radixweb!
ON THIS PAGE
- What is a Cloud App?
- Top Features of Cloud Apps
- Benefits of Cloud-Based Applications
- Limitations of Cloud-Based Applications
- Significant Use Cases of Cloud Apps
- What is a Web App?
- Top Features of Web Apps
- Benefits of Web Applications
- Limitations of Web Applications
- Significant Use Cases of Web Apps
- Web App vs Cloud App: A Quick Comparison
- Cloud App vs Web App: A Brief Table
- Cloud App vs Web App: Who Wins?
- Unlock the Best Option with Radixweb!
Quick Summary: Cloud apps and web apps power how users interact with tech; however, they’re not the same. From scalability to architecture, each serves different needs. And choosing the right one isn’t just a technical decision; it’s a strategic move defined by your business vision, user expectations, and operational workflows. In this article, you’ll explore the differences between web and cloud applications to help you pick the best option for your digital future.
As organizations continue to digitalize their operations, business analysts and product managers are often at the crossroads around which type of applications to build and deploy for their business. And one of the most common dilemmas they face is choosing the best option between web apps and cloud apps.
While the line between these terms often gets blurred, they both represent different digital transformation approaches with varying implications in terms of security, scalability, user experience, and expense. Understanding these differences is imperative for driving strategic planning that aligns with your business vision, ensures long-term success, and optimizes performance.
Being a pioneer in the IT industry for over two decades, we’ll help you explore the key differences between cloud apps and web apps. This article also breaks down their benefits and limitations for enterprise-level solutions and offers actionable insights to help business analysts and product managers make sound decisions for their organizations.
What is a Cloud App?
A cloud application is a digital solution that functions and operates on remote servers. These apps are hosted on the internet, so there’s no need to install them locally on a user's device. Cloud-based applications depend on cloud computing architecture to store, process, and handle data, which helps users access the app and its resources via a dedicated client or web browser.
Cloud-based apps are highly advanced web applications. However, it relies on web browsers. It can be customized only when it is connected to the cloud. This is done by web interfaces that are used to access cloud-based applications.
Top Features of Cloud-Based Applications
When developing cloud apps, it is important to integrate certain features and functionalities to ensure scalability, efficiency, and security. The following are the top features of these apps:
- It comes with online cloud data storage, which makes it possible to store data digitally and use it later, even when offline.
- Data can be cached locally for further use from a web browser or custom-built mobile apps.
- Cloud-based applications are user-friendly and support the prerequisites of customers, including security, data compression, and backup schedules.
- It also supports the access of different platforms for application development, on-demand computing cycles, etc.
- It supports different types of user requirements.
- It is easy to operate from any device with an internet connection on the browser, including desktop and mobile phones.
Advantages of Cloud-based Apps
When it comes to web app vs cloud app, the latter offers excellent business opportunities. From network capabilities to on-demand services and accessibility of shared resources, the cloud-based servers deliver multiple benefits.
Some of the significant ones include:
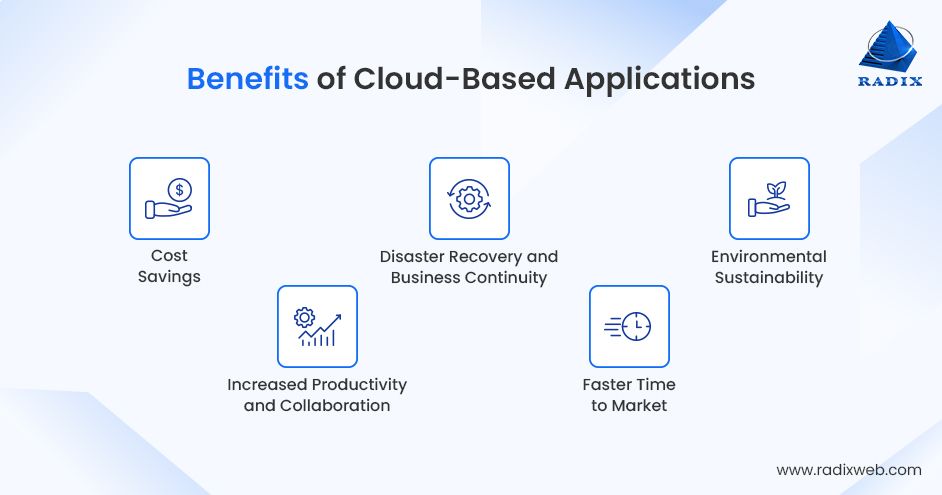
Cost Savings
Cloud app development minimizes the need for organizations to invest in costly on-premise infrastructure, software, and hardware.
Increased Productivity and Collaboration
These apps often come with real-time collaboration functionalities that help employees from different regions work together on the same projects or files.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
They often acquire in-built disaster recovery solutions, where your data is frequently backed up and can be rapidly restored in case of disaster or failure.
Faster Time to Market
Cloud service providers offer pre-built tools and infrastructure that speed up the application development lifecycle.
Environmental Sustainability
Many cloud providers today operate eco-friendly data centers and use low-carbon energy sources to support their infrastructure requirements.
Disadvantages of Cloud-Based Applications
Cloud app development is transforming how businesses functions, offering cost savings, flexibility, and scalability. But on the flip side, they acquire their fair share of limitations. So, before going all-out with the cloud, it’s crucial to understand the potential drawbacks, including:
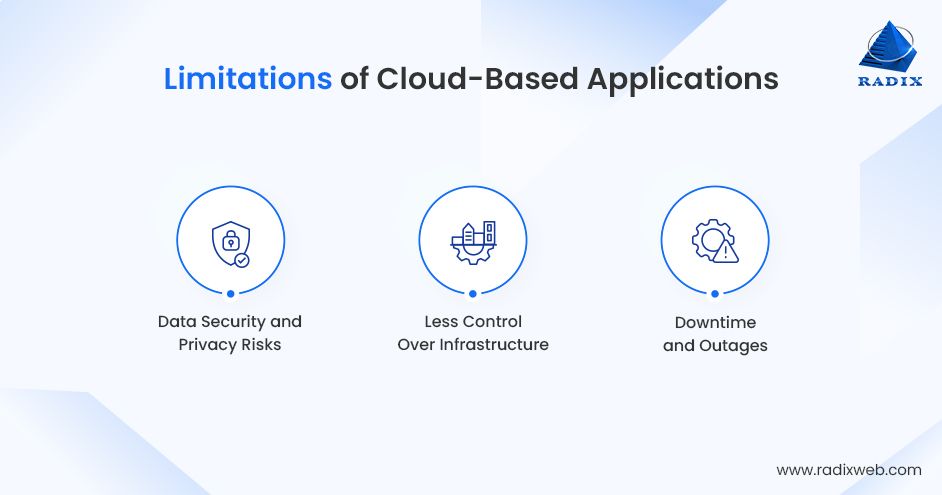
Data Security and Privacy Risks
While the majority of cloud apps come with robust security, no system is entirely immune to violations. This could risk confidential data, particularly if security protocols aren’t rock-solid.
Less Control Over Infrastructure
With cloud services, you’re necessarily renting someone’s tech architecture. This means very little control over how to manage, update, and customize the infrastructure.
Downtime and Outages
Even the biggest cloud service providers – Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and AWS – can sometimes experience downtime. So, if the servers go down, so does your access.
Industry-Specific Uses Cases of Cloud Apps
Cloud-based applications are a significant component for organizations working across different industrial vectors. Following are some of the key industry-specific use cases of cloud applications:
Finance and Banking
- Fraud Detection- Machine learning algorithms hosted on the cloud app platform help assess transactions in real-time, which recognizes patterns that might indicate fraudulent activities.
- Digital Banking Platforms- These apps help clients manage accounts, access financial services, and transact anywhere, anytime.
Healthcare
- Telemedicine Platforms- These apps allow health tracking, remote monitoring, and virtual consultations, which ensures seamless healthcare accessibility in remote areas.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) Systems- Cloud-based EHR solutions help healthcare experts manage and access patient data remotely for better care and real-time updates.
Education
- Virtual Classrooms and Webinars- The collaboration and video conferencing tools help with engaging sessions and remote learning for students.
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) - LMS platforms help teachers and students interact, track progress, submit assignments, and access materials.
Retail and E-Commerce
- E-commerce Platforms – Cloud-based e-commerce systems provide higher scalability for enterprises during high-traffic cases like holidays or sales.
- Inventory Management Systems – These apps help retailers track inventory in real time, which improves supply chain management and minimizes stockouts or overstock.
Government
- Disaster Response and Management - Cloud app platforms help with real-time coordination and data exchange among government organizations during emergencies.
- E-Government Services – These apps facilitate online citizen services such as tax filing, document submission, and other administrative services.
Telecommunications
- 5G and Edge Computing - Telecom organizations use these apps to implement and manage edge computing and 5G networks and minimize latency.
- Unified Communication Platforms – These advanced apps offer messaging, video, and voice services, which help remote businesses and teams to collaborate seamlessly.
What is a Web App?
A web application is a digital asset that operates in a web browser. Unlike conventional desktop apps, which you must install on a local computer, these apps are accessed via the internet using browsers like Edge, Safari, Firefox, and Chrome.
Developing web apps is like experiencing perfect integration of server-side (.NET and PHP) and client-side (Adobe Flash and HTML) scripts. Moreover, these apps mainly depend on the browsers and their server components, which further receive backend infrastructure support.
Web apps also feature convenience and allow users to access an app from anywhere they want with the computing model's help.
Top Features of Web-Based Applications
You can expect the global web app development market to value around USD 250.91 billion by 2030; kudos to its evolving features and functionalities. Let’s now go through the top features of these applications that make them widely adopted, flexible, and powerful across different industries:
- It works on different devices – smartphone, tablet, laptop, or desktop - with a web browser.
- It's accessible 24/7 from any location with a stable internet connection; hence, it is a good choice for on-the-go users, global teams, and remote work.
- The data is stored and protected on the central server, which minimizes the vulnerabilities of stolen or lost devices.
- It helps support multiple users simultaneously, hence, an adequate option for chat systems, real-time data sharing, and team collaboration.
- Due to its powerful web app architecture, you can easily scale resources and functionality as user demand grows.
- Stores all application and user data in a single place, which helps simplify analytics, reporting, and backup, ensuring consistency.
Advantages of Web Applications
Web-based applications help businesses to interact with their clients more efficiently. These apps can make it seamless to track and measure data, which is vital to streamline business operations. Following are some of the best benefits of web apps:
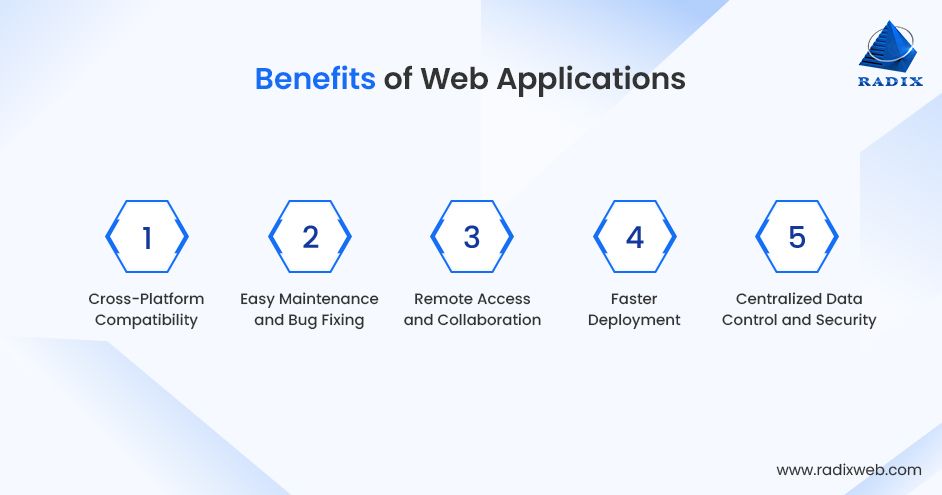
Cross-Platform Compatibility
These apps are compatible with operating systems and devices easily accessible to a more significant user base. You can access these apps on iOS, Android, Linux, macOS, and Windows without adopting platform-specific development.
Easy Maintenance and Bug Fixing
Since web apps work centrally on web servers, your development team can quickly recognize and rectify any bugs and issues without making users install updates.
Remote Access and Collaboration
The remote access feature facilitates seamless collaboration. It also helps team members work on the same app, which aligns remote work facilities and fosters better teamwork.
Faster Deployment
These apps can be published rapidly; you don't need to go through all app store approval processes. Once your web app development is done, you can deploy it and make it instantly available to users worldwide.
Centralized Data Control and Security
Businesses can have complete control over their data with centralized storage. Also, it's easy to enforce compliance (GDPR, HIPAA), access controls, and security policies.
Disadvantages of Web Applications
While web apps are full of potential, they still acquire some trade-offs. The following are some significant disadvantages:

Browser Compatibility Issues
Web apps might work differently across different browsers. So, it's significant for developers to consider cross-browser inconsistencies and bugs.
Security Risks
Being accessible and online through a browser can make your web application security more vulnerable to hackers and cyberattacks.
Potential SEO Drawbacks
In contrast to traditional websites, complicated web apps, particularly single-page apps, might face challenges with SEO. It needs additional work to ensure that your content is search engine accessible.
Industry-Specific Uses Cases of Web Apps
Following is a breakdown of industry-specific use cases of these apps, which reveals how they help with real-world concerns and improve workflows:
Hospitality and Travel
- Online Booking Engines – This software helps book activities, flights, and rooms easily. It minimize dependence on third-party platforms and amplifies direct revenue generation.
- Property Management Systems - This platform helps automate availability, housekeeping, and check-ins, which further minimizes staffing expenses and simplifies operations.
Real Estate
- Property Listing Platforms – The platform helps display real estate properties with clear photos, videos, and filters and helps attract buyers by providing rich experiences.
- Mortgage Calculators – This digital tool helps users estimate remunerations and affordability, which further educates prospects and speeds up decision-making.
Manufacturing and Logistics
- Order Tracking Systems – It helps customers with real-time progress and status of their shipments, which minimizes support inquiries and builds trust.
- Production Monitoring Dashboards – It tracks equipment status, downtime, and output, which further prevents any unplanned maintenance and bottlenecks.
Creative, Media, and Marketing
- Content Management Systems (CMS)- The software helps publish and manage marketing materials, websites, blogs, guest posts, etc. It empowers non-technical teams to modify the content easily and whenever needed.
- Design Collaboration Tools – This tool helps teams to work on ads, wireframes, and visuals in real-time, which minimizes miscommunication and speeds up the creative processes.
Legal and Compliance
- Case Management Systems – It helps track legal cases, client interactions, documents, and deadlines, enhancing client services and minimizing administrative workload.
- Compliance Monitoring Tools – These tools help track risk indicators and internal policy adherence, ensuring industry compliance, minimizes liability, and supports audits.
Government and Public Sector
- Citizen Services Portals – It helps citizens access services like support programs, IDs, and permits, which further minimizes in-person traffic and optimizes service delivery.
- E-voting and Survey Platforms – This tool helps securely conduct digital elections and collect citizen feedback, which improves efficiency and participation.
Cloud Application vs Web Application: A Basic Brief Comparison
As business analysts and product managers, making the right choice between web apps and cloud apps needs a deep understanding of how these apps impact scalability, security, cost efficiency, and overall user experience:
Architecture
Web apps typically use a traditional client-server architecture. This architecture is usually straightforward but faces system delays as the apps scale in demand or complexity.
On the contrary, cloud-based applications use more complex architectures, like cloud-native, that deploy microservices architecture, distributed systems, and containers. Cloud apps are developed to manage fault tolerance, redundancy, and high availability.
Accessibility
Web applications are majorly accessed via a web browser. You must visit a website (URL) to use your app. You don't need to install anything on your device, which makes it seamless to access virtually from any device.
On the other hand, you can access cloud applications through a web browser; however, they often come with dedicated mobile and desktop apps. This allows users to use the app on different devices, such as tablets, smartphones, and computers.
Hosting
Web apps are generally hosted on standard web servers. This means you can maintain them easily but may face certain challenges regarding integration with other technologies, flexibility, and scalability. These apps depend either on a single server or a set of web servers.
On the contrary, cloud-based applications are hosted on different cloud computing platforms like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, or AWS. These platforms help these apps to scale automatically as per the requirements.
Internet Requirement
Web apps need an active internet connection to operate. They don't store all the data on your device, and all the processing is done with the help of a web server. So, if your internet is not stable or slow, the app might not work its best or at all.
Cloud apps are designed to experience the benefits of cloud computing infrastructure; many can even work offline. When you don't have internet, the app stores the data locally and syncs it once you're online.
Resource Utilization
Since web app is hosted on a single server or set of small servers), their resource utilization is forced by the challenges of the server hosting your app.
Cloud apps use computing resources like databases, storage, and processing power to improve user experience and performance. They are proficient in managing large data volumes and complex tasks by distributing work across multiple cloud servers.
Technology Stack and Frameworks
Web apps generally use standard web technologies like JavaScript, CSS, and HTML for frontend development and Node.js, Ruby, Python, and PHP for backend development. These apps are often developed using popular web frameworks like Laravel, Ruby on Rails, Django, Angular, and React.js.
Cloud apps deploy cloud computing technologies and might include APIs, microservices, containerization, and serverless computing. Cloud app development uses modern frameworks built for distributed systems, including Serverless frameworks, Dockers, Kubernetes, and Spring Boot.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Web apps integrate standard security measures like HTTPS, firewalls, and SSL/TLS encryption to protect data during transfer. And compliance may depend on how your app is hosted. For instance, if your data is stored, it is essential to meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA or GDPR, depending on the industry and region.
Cloud apps leverage advanced security measures the cloud service providers offer, which include multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity and access management (IAM), and end-to-end encryption. Also, major cloud providers comply with standards, including PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, and ISO 27001.
Offline Functionality
Web apps need an active internet connection to work. However, developing progressive web apps (PWAs) comes with limited offline functionality by caching content and enabling engagement even without proper internet.
Cloud apps come with robust offline functionalities. For instance, Google Docs helps end-users to work offline and sync data to the cloud when the connection is back.
Data Storage
Data is stored on a central server. When the app is accessed, the data is collected back from the server. Web apps typically depend on server-side databases for storage, which can get slow if the internet gets slow.
On the contrary, cloud app platforms use distributed cloud storage, which ensures high availability and redundancy. These apps can also experience the benefits of large-scale databases, such as Firebase, Google BigQuery, or AWS DynamoDB.
Development Cost Implications
The cost to develop web apps is generally less because it requires minimal infrastructure. You can build them with the help of standard web frameworks and technologies, and the architecture is usually less complex.
- Basic or simple web apps might range from around USD 10,000 to USD 50,000.
- Mid-level or custom, feature-rich web apps can cost around USD 50,000 to USD 200,000+.
- Complex or enterprise-grade web apps often exceed USD 200,000 depending on advanced features and scale.
On the other hand, cloud-based applications are likely to be more expensive as they need more advanced infrastructure and technologies. Developers must collaborate with cloud service providers to ensure higher productivity, security, and versatility.
- MVPSs or smaller cloud-based apps usually start around USD 15,000 to USD 50,000.
- Full-featured, cloud apps integrated with few advanced features commonly range from USD 70,000 to USD 300,000+.
- Enterprise-grade or highly complex cloud apps may value around USD 300,000 and can go up to USD 750,000 or even more, as it comes with advanced services or extensive integrations.
In summary, web apps generally cost 30–40% less to develop than cloud apps, but cloud apps tend to deliver higher long-term returns due to scalability and automation
Web App vs Cloud App: A Quick Comparison Table
| Parameters | Cloud App | Web App |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Cloud-native with microservices, containers, and high availability | Traditional client–server; limited scalability |
| Accessibility | Browser + dedicated mobile/desktop apps | Browser-based via URL |
| Hosting | Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) | Standard web servers |
| Internet Dependency | Supports offline use with data sync | Requires constant internet |
| Resource Utilization | Dynamically scales across cloud resources | Limited by server capacity |
| Tech Stack | Microservices, APIs, Docker, Kubernetes, Serverless | HTML, CSS, JS, Node.js, Django, React |
| Security and Compliance | Advanced security with built-in compliance standards | Basic security; compliance depends on setup |
| Offline Functionality | Strong offline capabilities | Minimal (via PWAs) |
| Data Storage | Distributed cloud storage with redundancy | Centralized server storage |
| Development Cost | Higher cost ($15k–$750k+) | Lower cost ($10k–$200k+) |
Cloud App vs Web App: Who Wins the Battle?
Choosing the winner - web-based vs cloud-based apps - can be a crucial yet confusing decision largely depending on your business objectives, users, infrastructure, and budget. The following are the key factors you should consider when making the decision:
1. Scalability - Scaling is possible in web apps but is usually restricted by the infrastructure hosted. Cloud apps are designed to scale across multiple use bases and regions using cloud service providers.
2. Infrastructure and Maintenance – Web apps help manage most monitoring, updates, and hosting unless you use PaaS. And cloud apps here benefit from managed services, load balancing, monitoring, and auto-scaling.
3. Integration and Extensibility – Web apps can integrate but might need manual work. Cloud apps are seamless when integrated with third-party services.
4. Cost – Web apps might have lower initial expenses, but scaling can be expensive. Cloud apps follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Make the Optimal Decision with RadixwebWhether you’re a product manager or business analyst, choosing between a cloud and a web app relies on a thorough comprehension of your business goals, user requirements, and technical needs. While web apps are best known for accessibility and simplicity, cloud apps come with advanced features and robust security, which makes them the best fit for businesses looking for dynamic, future-proof solutions.Radixweb can help you decide between a web-based or a cloud-based application and quickly help you achieve your targets cost-effectively. And whatever approach you choose, our experts will help you develop custom applications to meet your business objective and technical specifications. We bring you unmatched, deep expertise and a knowledge base spanning diverse technology and frameworks.Contact us to make the right decision – cloud apps vs web apps.
FAQs
Is a cloud app the same as a web app?
What are some popular examples of web apps and cloud apps?
Do web apps need cloud infrastructure?
Which is better for startups: a web app or a cloud app?
When should a business switch from web app to cloud app?
Ready to brush up on something new? We've got more to read right this way.