Read More

Discover what’s next for AI in healthcare in 2026 - Get Access to the Full Report
ON THIS PAGE
- What is AI in Transportation?
- AI in Transportation: How Has It Evolved Over The Years?
- AI in Transportation: Top Use Cases
- AI in Transportation: Benefits for Companies and Customers
- AI in Transportation: Key Industry Challenges
- AI in Transportation: Implementation Roadmap
- Getting Started with AI in Transportation
ON THIS PAGE
- What is AI in Transportation?
- AI in Transportation: How Has It Evolved Over The Years?
- AI in Transportation: Top Use Cases
- AI in Transportation: Benefits for Companies and Customers
- AI in Transportation: Key Industry Challenges
- AI in Transportation: Implementation Roadmap
- Getting Started with AI in Transportation
At a Glance: Artificial Intelligence is reshaping the transportation industry by enabling safer mobility, smarter traffic management, optimized logistics, and predictive operations across road, rail, air, and maritime networks. In this blog, we explore how the use of AI in transportation has evolved, real-world user cases, benefits, challenges, and a step-by-step implementation roadmap. Dive in to see how organizations can build intelligent, future-ready transportation systems.
- In Singapore, AI-powered traffic lights have reduced urban congestion by 20%. The result? Commute times have improved and emissions have lowered.
- In Los Angeles, predictive analytics are optimizing traffic flow. The result? The average travel time went down by 12%.
- Companies like DHL AI for predictive maintenance and route optimization. The result? DHL could cut miles traveled by 26%.
Now, these are not isolated examples. AI in transportation is rapidly becoming mainstream. According to recent AI statistics, more than 72% of all businesses worldwide are already implementing AI-driven solutions. This includes transportation businesses too, where AI is being used for traffic management, fleet operations, and even supply chain optimization.
Intelligent traffic systems, connected infrastructure, autonomous vehicles, and predictive logistics are becoming the norm. Overall, AI is reshaping how people and goods move, making transportation faster, safer, and much more efficient.
In this blog, we will walk you through the ‘what’, ‘why’, and ‘how’ of AI in transportation, but what the future of AI in transportation looks like. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the industry and a plan that you can start implementing today. Read on.
What Is AI in Transportation?
AI in transportation is the technology that allows transportation systems to think, predict, and adapt in real time. Using machine learning, computer vision, predictive analytics, and natural language processing, AI helps plan, operate, and optimize movement across roads, railways, air travel, maritime routes, and multimodal networks.
Instead of relying on fixed rules, AI-driven transportation systems continuously analyze live and historical data from vehicles, sensors, GPS devices, traffic cameras, and weather feeds. This enables them to anticipate congestion, optimize routes, improve safety, and support autonomous decision-making as conditions change.
The role of AI in transportation extends beyond passenger mobility. It powers smart traffic management, autonomous vehicles, and predictive maintenance, while also transforming logistics and supply chains through demand forecasting, fleet management, and real-time shipment visibility.
Simply put, AI turns transportation from a reactive system into a predictive, self-improving mobility ecosystem, shaping the future of smarter, safer, and more connected transportation.
Evolution of AI in Transportation
AI in transportation has evolved alongside advances in computing, data availability, and connectivity. What began as basic automation has progressed into intelligent, data-driven systems that support real-time decision-making across transportation networks.
Early Automation Era (Pre-2010): Rule-Based Transportation Systems
- Transportation relied on fixed rules and manual decision-making.
- Early applications included traffic signal timers, GPS navigation, and fleet tracking.
- AI had a minimal role and could not learn from data.
Data-Driven Optimization Phase (2010–2018): Predictive Intelligence Emerges
- Sensors and GPS enabled large-scale data collection for transportation systems.
- ML improved route planning, traffic prediction, and fleet management.
- AI in logistics supported demand forecasting and delivery optimization.
- Applications prioritized operational efficiency over autonomy.
Intelligent & Connected Mobility Era (2019–Present): Real-Time AI Systems
- Advances in deep learning and computer vision enabled real-time decision-making.
- Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic & predictive maintenance deployed.
- AI platforms connected vehicles, infrastructure, and users in unified systems.
- Adoption expanded across road, rail, air, and maritime transportation.
- Safety, sustainability, and operational reliability became primary benefits.
Future Outlook: Autonomous, Ethical, and Adaptive Transportation
- Transportation systems are expected to become adaptive, autonomous, and data-driven.
- AI will enable coordinated operations between vehicles and urban infrastructure.
- Regulatory frameworks and ethical guidelines will guide AI adoption.
- Explainable and secure AI platforms will help overcome adoption barriers.
- AI will expand mobility services, logistics automation, and smart city planning.
As this progression shows, AI in transportation has moved from basic automation to a core capability supporting modern mobility systems. Its continued development will shape how transportation networks operate, scale, and respond to future demands.
Key Use Cases of AI in Transportation
The expanding AI in transportation ecosystem is driven by practical, high-impact applications that solve real-world mobility challenges. Across public and private sectors, organizations are adopting intelligent systems to enhance safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
Below are the most prominent AI in transportation use cases shaping modern mobility.
| AI Use Case | What AI Does | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomous Vehicles | Enables perception and driving decisions | Improves safety and automation |
| Traffic Prediction | Forecasts congestion in real time | Reduces delays and fuel use |
| Route Optimization | Selects efficient routes dynamically | Lowers costs and delivery time |
| Predictive Maintenance | Detects failures before breakdowns | Reduces downtime and repairs |
| Public Transport Planning | Forecasts demand and adjusts schedules | Improves service reliability |
| Freight & Logistics | Tracks shipments and forecasts demand | Increases supply chain resilience |
| Safety Monitoring | Detects incidents and hazards | Improves response time |
| Smart Parking | Predicts parking availability | Reduces congestion |
These AI in transportation examples demonstrate how intelligence is embedded across the entire mobility value chain.
Benefits of AI in Transportation
The rapid adoption of AI in transportation is driven by its ability to solve long-standing mobility challenges while unlocking new levels of efficiency, safety, and sustainability. Across public infrastructure, commercial fleets, and logistics networks, organizations are realizing measurable value through intelligent, data-driven transportation systems.
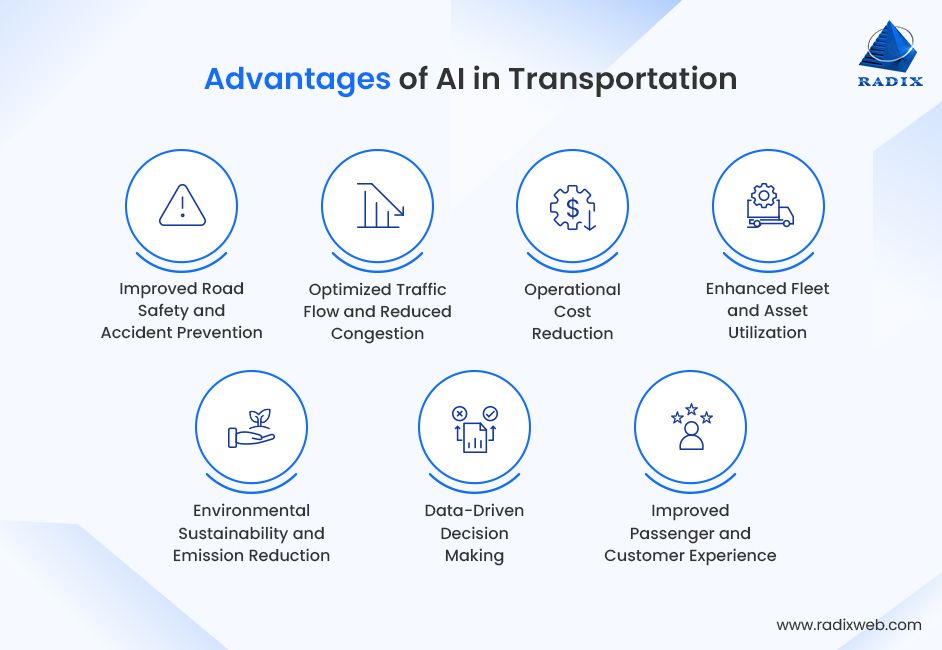
Improved Road Safety and Accident Prevention
One of the strongest benefits of AI in transportation is improved road safety. AI systems analyze real-time data from cameras, sensors, and vehicles to detect risks early. This strengthens the role of AI in transportation in reducing accidents and fatalities.
Optimized Traffic Flow and Reduced Congestion
AI in smart transportation systems predicts congestion and adjusts traffic signals dynamically. Vehicles are rerouted in real time to reduce delays. This use of AI in transportation improves traffic flow and travel reliability.
Operational Cost Reduction
AI in transportation reduces operating costs through intelligent routing and predictive maintenance. Fuel consumption and downtime decrease. AI in logistics and supply chain operations further improves delivery efficiency.
Enhanced Fleet and Asset Utilization
AI in transportation analyzes vehicle performance and demand patterns to improve scheduling. With proper logistics software development for transportation, fleet availability increases while idle time drops. This reinforces the role of AI in transportation for large-scale fleet management.
Environmental Sustainability and Emission Reduction
AI in transportation lowers emissions by optimizing routes and reducing idling. Smart traffic management supports sustainability goals and regulatory compliance.
Data-Driven Decision Making
AI applications in transportation convert large data volumes into actionable insights. Operators and planners make faster, more accurate decisions across operations.
Improved Passenger and Customer Experience
Real-world AI in transportation examples show improved arrival accuracy and service reliability. Customers experience fewer delays and better transparency.
Together, these benefits show how AI in transportation has become a foundational capability for building safer, more efficient, and scalable mobility systems.
Challenges of AI in Transportation
While AI in transportation offers significant benefits, organizations face multiple challenges when deploying and scaling intelligent mobility solutions. These challenges span technology, data, regulation, ethics, security, and organizational readiness, and must be addressed for successful adoption.
1. Data Quality, Availability, and Integration Challenges
AI in transportation relies on accurate, real-time data from vehicles, sensors, and infrastructure, but transportation data is often fragmented and inconsistent.
- Fragmented data across systems, vendors, and stakeholders
- Poor data quality, missing data, and outdated formats
- Limited real-time data availability
- Legacy infrastructure restricting data access
- Data silos in AI in logistics and supply chain operations
How to tackle it:
Organizations must implement strong data governance, standardize data formats, and invest in unified data platforms to support reliable AI applications in transportation.
2. Infrastructure and Technology Limitations
Advanced AI in smart transportation systems require connected infrastructure, computing power, and real-time processing capabilities that many regions still lack.
- Insufficient sensor and IoT deployment
- Limited network connectivity and bandwidth
- Lack of edge and cloud computing readiness
- Integration challenges with legacy systems
- Scalability issues in complex urban environments
How to tackle it:
Modernizing legacy systems and infrastructure with AI and adopting scalable cloud-edge architectures are essential to overcoming infrastructure barriers to AI in transportation.
3. Regulatory and Compliance Complexity
Transportation is highly regulated, and AI transportation regulations continue to evolve across regions, creating uncertainty for organizations.
- Inconsistent regulations across countries and jurisdictions
- Unclear rules for autonomous vehicles and AI-driven decisions
- Compliance challenges related to data usage and safety standards
- Liability uncertainty in AI-driven incidents
- Slower innovation due to regulatory ambiguity
How to tackle it:
Close collaboration with regulators and proactive compliance strategies help organizations align Artificial intelligence in transportation industry solutions with evolving legal frameworks.
4. Ethical, Bias, and Transparency Risks
As AI systems influence safety-critical decisions, ethical issues with AI in transportation become increasingly important.
- Algorithmic bias caused by unbalanced training data
- Lack of transparency in AI decision-making
- Limited explainability in autonomous systems
- Accountability challenges in safety incidents
- Reduced public trust due to opaque models
How to tackle it:
Responsible AI practices, explainable models, and continuous bias monitoring are essential to addressing ethical issues with AI in transportation.
5. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
Connected transportation systems process sensitive data, increasing exposure to cyber threats and privacy risks.
- Vulnerability of connected vehicles and infrastructure
- Risks to passenger, vehicle, and logistics data
- Increased attack surfaces in AI in smart transportation systems
- Supply chain exposure in AI in logistics and supply chain networks
- Compliance pressure from global privacy regulations
How to tackle it:
Strong cybersecurity frameworks, data encryption, and privacy-by-design approaches are critical for securing AI applications in transportation.
6. Cost, Talent, and Organizational Readiness
The adoption of AI in transportation requires significant investment and specialized expertise that many organizations lack.
- High costs of AI development and deployment
- Shortage of AI and data science talent
- Challenges integrating AI with existing operations
- Resistance to change from legacy processes
- Long timelines for measurable ROI
How to tackle it:
Phased AI adoption, workforce upskilling, and strategic partnerships help reduce barriers to AI adoption in mobility.
Addressing these challenges of AI in transportation requires a balanced approach that combines technology investment, responsible AI design, regulatory alignment, and organizational readiness. Organizations that proactively tackle these barriers are better positioned to scale safe, ethical, and high-impact AI-driven transportation systems.
Implementation Roadmap for AI in Transportation
Adopting AI in transportation requires a structured, business-aligned approach. This five-step roadmap outlines how transportation and mobility leaders can implement AI solutions in a scalable, responsible, and value-driven way.
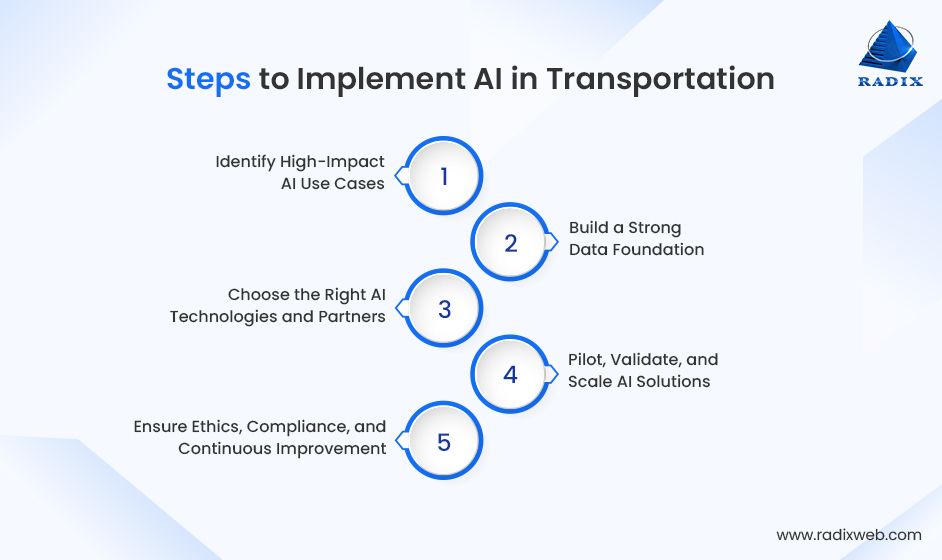
Step 1: Identify High-Impact AI Use Cases
The first step in adopting AI in transportation is identifying where it can deliver measurable value. Organizations should assess operational bottlenecks, safety risks, cost drivers, and customer experience gaps. Common starting points include route optimization, predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and fleet management. Prioritizing clear AI use cases reduces risk and accelerates ROI.
Step 2: Build a Strong Data Foundation
AI success depends on data quality, availability, and accessibility. Transportation organizations must consolidate data from vehicles, sensors, GPS systems, traffic infrastructure, and enterprise platforms into a unified data architecture. This is especially critical for AI in logistics and supply chain, where fragmented data limits visibility. Strong data governance, integration pipelines, and real-time processing enable reliable AI application in transportation at scale.
Step 3: Choose the Right AI Technologies and Partners
With data readiness in place, organizations should select AI programming languages aligned with business goals. This may include machine learning for prediction, computer vision for monitoring, or optimization algorithms for planning. Many organizations partner with experienced providers who understand the Artificial intelligence in transportation industry. Strategic partnerships help reduce technical complexity and barriers to AI adoption in mobility.
Step 4: Pilot, Validate, and Scale AI Solutions
When building AI software, the solutions should be tested through controlled pilot programs before full deployment. Pilots validate model accuracy, system performance, and operational impact while minimizing risk. Real-world AI in transportation examples show that iterative testing improves adoption and confidence.
Step 5: Ensure Ethics, Compliance, and Continuous Improvement
Long-term success with AI in transportation requires responsible governance. Organizations must align solutions with AI transportation regulations and address ethical issues with AI in transportation, including transparency, bias, and accountability. Continuous model training, performance evaluation, and cybersecurity updates ensure systems remain accurate, compliant, and resilient.
Getting Started with AI in TransportationThe global AI in transportation market is projected to grow from around USD 9 billion in 2025 to nearly USD 71 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of over 22% as demand for autonomous systems, traffic management, and predictive solutions expands. As competition intensifies and customer expectations rise, the role of AI in transportation has shifted from optional innovation to business necessity.But achieving value from AI in transportation requires strategy and the right execution partner. At Radixweb, we have build several enterprise‑grade AI solutions including those for the transportation solutions, including AI in logistics and supply chain, from use case identification and data readiness to compliant, ethical deployment.If you are not sure where to start from or have an idea that you’d like to discuss for AI adoption in mobility, schedule a no‑cost consultation to accelerate your intelligent transportation initiatives. Our AI developers are ready to help you get started.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does it cost to implement AI in transportation systems?
How long does it take to see results from AI adoption in transportation?
Can AI be integrated with existing transportation management systems?
What internal capabilities are needed to manage AI solutions long term?
How do organizations measure ROI from AI in transportation initiatives?
Ready to brush up on something new? We've got more to read right this way.